
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 9-8000
CHAPTER 29
DIFFERENTIALS, FINAL DRIVES, AND DRIVING AXLES
Section I. CONVENTIONAL DIFFERENTIALS
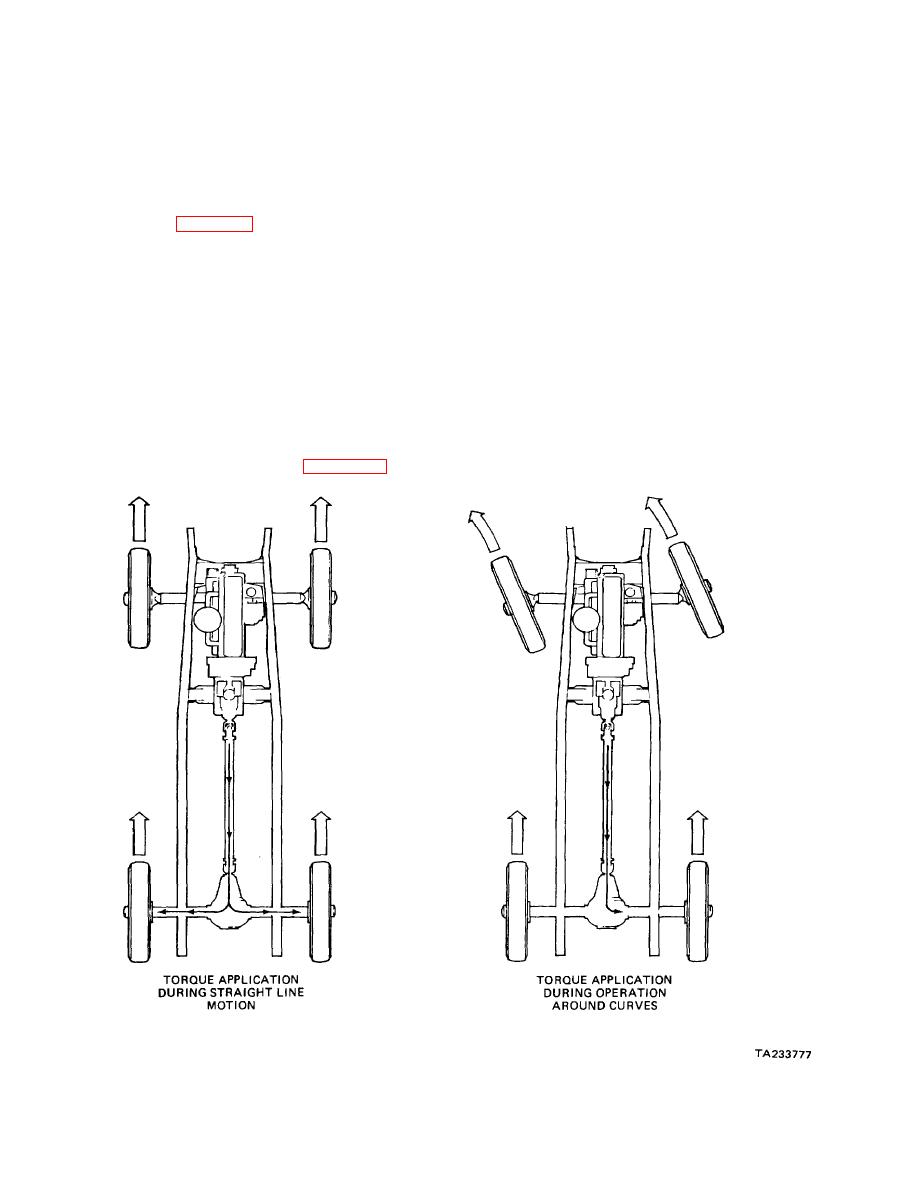
bevel drive pinion rotates the bevel drive ring gear and
29-1.
Purposes (Fig. 29-1).
the differential case to which the final drive gear is
bolted. The axle shafts are splined to the differential side
a. Transmit Torque to Axles. One of the purposes
gears. Were it not for the differential pinions, each
of the differential is to transmit engine torque to the drive
wheel, with its respective axle shaft and side gear, would
axles. The drive axles usually are on a rotational axis
rotate freely with respect to the differential case and
that is 90 degrees different than the rotational axis of the
bevel drive gear.
propeller shaft.
a. Straight Ahead. When both wheels are rotating
b. Divide Engine Torque. Another purpose of the
at the same speed, as they do on a smooth, straight
differential is to divide engine torque between the driving
road, the differential pinions do not rotate around their
wheels so that they are free to rotate simultaneously at
own axis but serve only to
varying speeds. This is important particularly if the
vehicle is not moving in a straight line.
29-2.
Principles of Operation
The
Figure 29-1. Differential Operation.
29-1
|
||
 |
||