
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
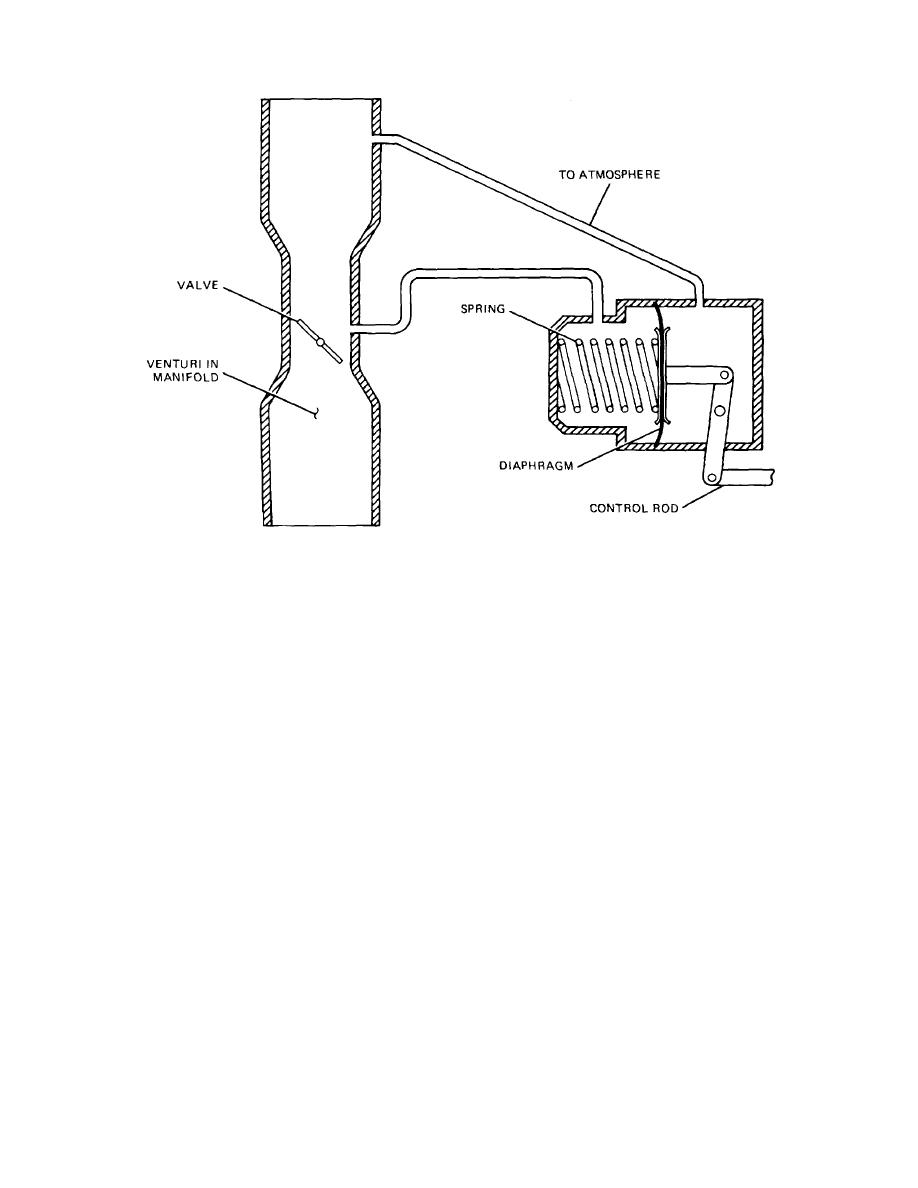 TM 9-8000
Figure 5-24. Vacuum Operated Governor.
The amount of pressure reduction depends on the
corresponding increase in the pressure differential on
position of the governor valve and speed of the engine.
both sides of the diaphragm. The increase in pressure
It is this pressure differential that positions the diaphragm
differential causes the diaphragm and the control rod to
and, consequently, the control rod of the injection pump.
move against the pressure of the spring toward the no-
The governor valve is controlled by a lever that is
fuel position.
The control rod's position will stabilize
connected by suitable linkage to the foot throttle. There
when equilibrium is achieved in the diaphragm unit.
is no mechanical connection between the foot throttle
When the engine is operating at wide-open throttle, the
and the control rod of the injection pump.
pressure differential will be almost zero and spring force
will position the control rack in the full-fuel position.
c. If the engine is operating under load and the
d. For any position of the governor valve between
speed (rpm) is below governed speed, the velocity of air
passing through the venturi is comparatively low and only
idling and full load of the engine, the diaphragm finds its
a slight pressure differential is present. This will cause
relative position.
Because any movement of the
the spring to move the diaphragm and the injector pump
diaphragm also is transmitted to the control rod, the
control rack toward the full-fuel position. As the engine
amount of fuel delivery definitely is controlled at all
speed picks up, the pressure differential on both sides of
speeds. The diaphragm is moved in the direction of
the diaphragm and the spring will achieve equilibrium
less fuel delivery as the pressure drop between the
and the position of the control rod will stabilize. The
chambers is increased. The spring will move the control
same operating principles will apply in reverse to prevent
rod in the direction of greater fuel delivery as the
engine overspeed. As the engine speed increases, the
pressure drop is decreased.
velocity of air through the venturi increases, causing a
TA233460
5-32
|
||
 |
||