
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
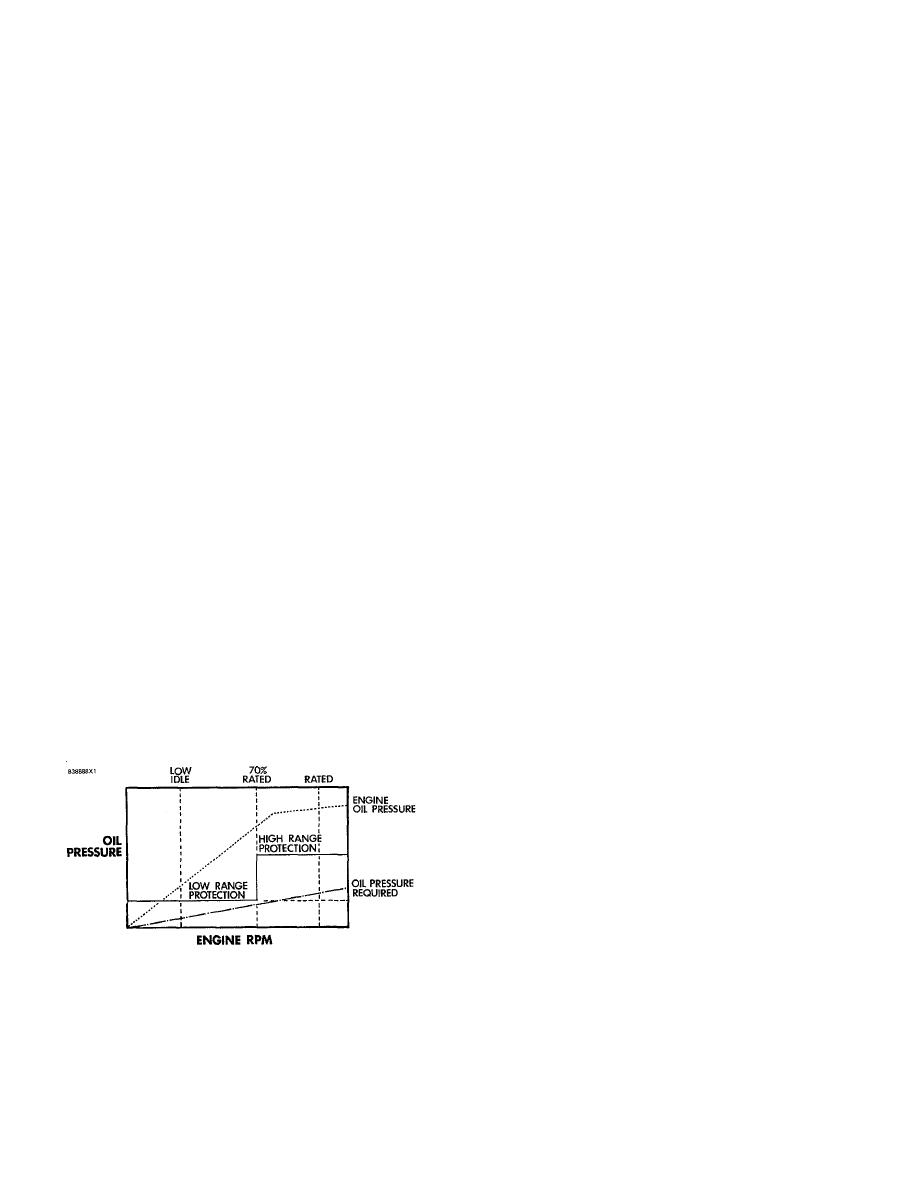 HYDRAMECHANICAL PROTECTIVE SYSTEM
SYSTEMS OPERATION
HYDRAMECHANICAL PROTECTIVE SYSTEM
The hydramechanical protective system is de-
From Figure 1, it can be seen that if only the low
signed as a self contained system separate from the
range oil pressure protection level was used for the full
engine governor. This system is used to activate an
speed range, the engine could operate at rated speed
alarm or shutdown an engine for low oil-pressure, high
with oil pressure below the required level. Also, if only
coolant temperature or engine overspeed conditions.
the high range oil pressure protection level was used for
the full speed range, the system would shutdown the
engine at low idle, since the engine oil pump develops
OVERSPEED
lower pressure at that speed. Therefore, the protective
system must operate between the required oil pressure
In general, an overspeed condition is the result
curve and the engine oil pressure curve. This is done
of a fuel system that fails to operate correctly. This in
with a step action of pressure versus speed.
turn allows the combustion system to get more fuel than
the engine load needs. The excess fuel can accelerate
The
hydramechanical
protective
system
the engine to a point that engine failure can be the result.
operates within the two ranges of engine oil pressure.
As engine speed increases, the minimum oil pressure
The rate of engine acceleration is controlled by
needed at the main bearings also increases. At low
several factors. Friction horsepower, attached inertial
engine speed, an alarm or fuel shutoff actuator will
loads and operating loads make up the main affects on
activate when oil pressure is reduced to within 140 35
acceleration. In most all cases, the protective system
kPa (20 5 psi). At high engine speeds, an alarm or fuel
must have a response time of less than one second.
Response time is the time interval between the
shutoff actuator will activate when oil pressure is reduced
overspeed and the actuation of the protective system.
to within 205 35 kPa (30 5 psi).
The protective system must provide this response under
different conditions such as engine start up at extreme
For a low oil pressure condition, the protective
ambient temperatures and under full load operation.
system activates an alarm or moves the fuel control
linkage, through the governor, to the "SHUTOFF"
For an overspeed condition the fuel control linkage is
position. The combustion air supply is not shutoff for this
moved to the "SHUTOFF" position and the engine
condition.
combustion air supply is stopped.
HIGH COOLANT TEMPERATURE
LOW ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
If the coolant temperature of an engine goes
As engine speed increases, the required oil pressure for
above a set limit, the protective system activates an
main bearing protection increases. The engine oil pump
alarm or moves the fuel control linkage to the
is a positive displacement type pump, therefore, engine
"SHUTOFF" position to shutdown the engine. The
oil pressure varies in direct proportion to speed until the
combustion air supply is not stopped under this
pump goes on controlled bypass.
condition.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The system consists of an emergency manual
shut- off, a shutoff control group, a diverter valve, a
thermostatic pilot valve, an air inlet shutoff and a fuel
shutoff actuator for the governor.
The air and fuel shutoff systems are separate
from each other to give complete engine shutdown for an
overspeed condition. If the engine fuel is held in the
"ON" position, the air inlet shutoff must work to shutdown
the engine.
FIGURE 1. TWO-STEP OIL
PRESSURE PROTECTION
211
|
||
 |
||