
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 9-8000
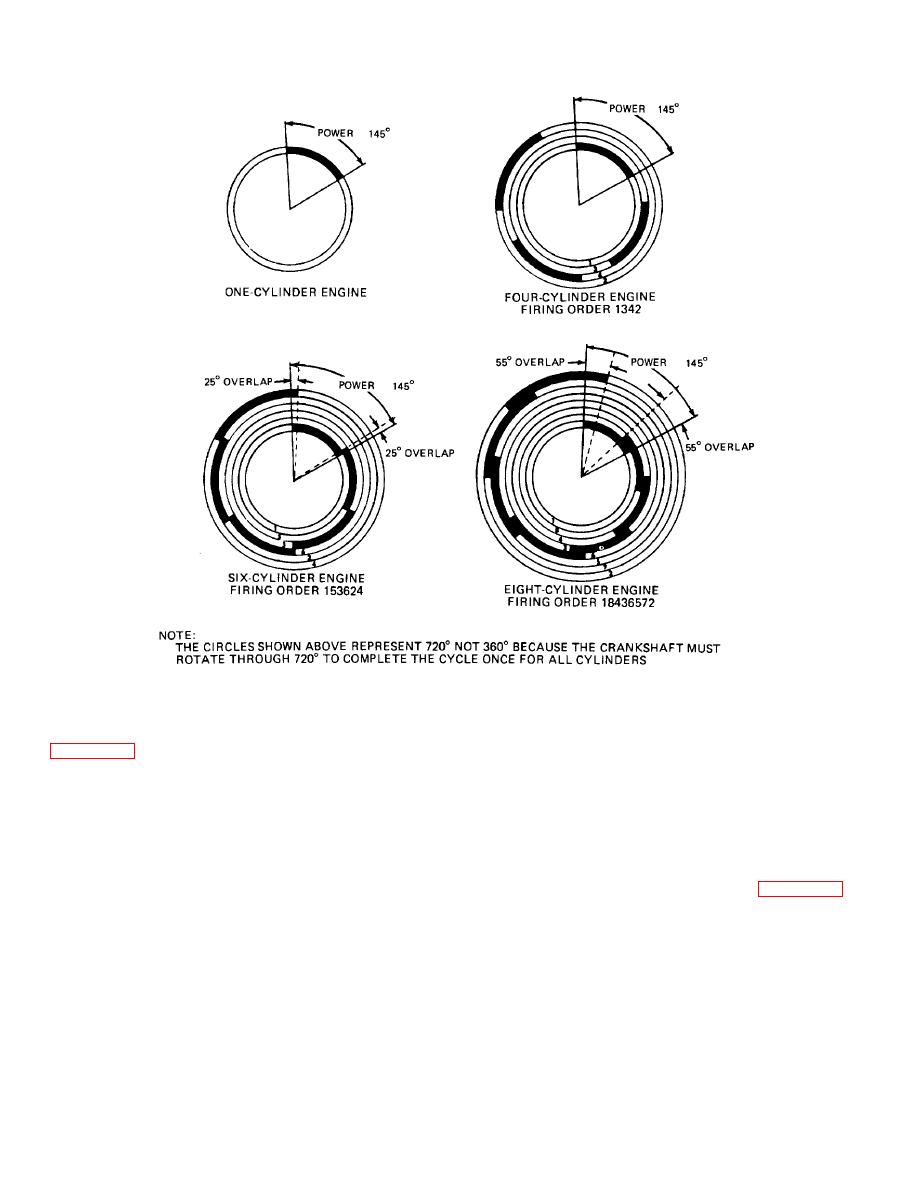
Figure 2-26. Power Delivery in One-, Four-, Six-, and Eight-Cylinder Engines
ders. An eight-cylinder engine has an even larger 55-
2-16. Piston Engine Versus Rotary Engine.
degree power overlap. It becomes very obvious from
a. General. A relatively new configuration of the
the smoother the power delivery will be.
gasoline engine, called the rotary, has reached the
automotive scene within the past 25 years. Its operating
. Power Increase. It also is obvious that the most
cycle is exactly the same as the piston engine, consisting
practical way to increase the power output of an engine is
of intake, compression, power, and exhaust operating
to make a lot of small cylinders instead of one big one. A
phases. But rather than having reciprocating pistons
multicylinder engine is not only smoother but more
rotating a crankshaft, it uses a triangular-shaped rotor
reliable also. This is because each piston weighs less
that rotates around Inside of a specially shaped housing.
than a comparable size single-cylinder engine. The
The basic rotary engine is illustrated in figure 2-27. As
constant changing of direction of the piston causes more
the rotor moves around the inside of the housing, it also
bearing wear if the piston is excessively heavy Also, the
rotates an offcenter or eccentric shaft through an internal
single-cylinder engine is not as smooth, which will
gear. The housing has intake and exhaust ports cast into
decrease not only the life of the engine, but also the
the housing in strategically located points.
equipment that it is operating.
TA233327
2-19
|
||
 |
||