
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 9-8000
raw unvaporized fuel to be introduced to the combustion
chambers. Because unvaporized fuel does not burn, it is
a. Combustion. To understand what is meant by
wasted. This reduces fuel economy and causes a
antiknock quality, first review the process of combustion.
condition known as crankcase dilution.
When any substance burns, it actually is uniting in rapid
chemical reaction with oxygen (one of the constituents of
b. Crankcase Dilution. Crankcase dilution occurs
air). During this process, the molecules of the substance
when the fuel that is not vaporized leaks past the piston
and oxygen are set into very rapid motion and heat is
rings and seeps into the crankcase. The unvaporized
produced. In the combustion chamber of an engine
fuel then dilutes the engine oil, reducing its lubricating
cylinder, the gasoline vapor and oxygen in the air are
qualities. A certain amount of crankcase dilution occurs
ignited and burn. They combine, and the molecules
in all engines during warm-up. It is not considered
begin to move about very rapidly as the high
harmful in normal quantities because it vaporizes out of
temperatures of combustion are reached.
The
the oil as the engine warms up. The vapors then are
molecules, therefore, bombard the combustion chamber
purged by the crankcase ventilation system (para 7-7).
walls and the piston head with a shower of fast moving
molecules. It is actually this bombardment that registers
c. Vapor Lock. Vapor lock is one of the difficulties
the heavy push on the piston and forces it downward on
experienced in hot weather when using highly volatile
the power stroke.
fuels. When fuel has a tendency to vaporize at normal
atmospheric temperature, it may form so much vapor in
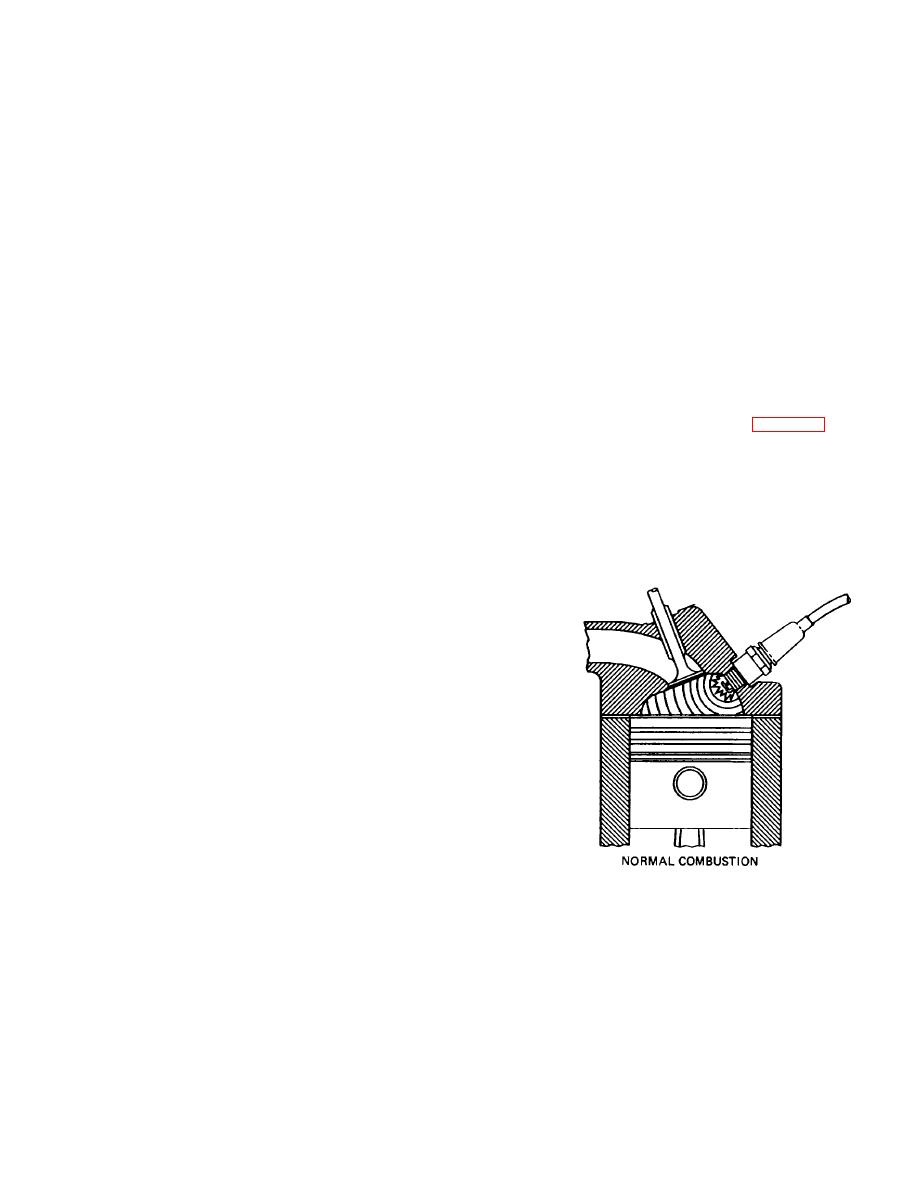
b. Combustion Process. The normal combustion
the fuel line that the action of the fuel pump will cause a
process in the combustion chamber (fig. 4-76) goes
pulsation of the fuel vapor rather than normal fuel flow.
through three stages when producing power. They are
Heat Insulating materials or baffles are often placed
as follows:
between the exhaust pipe and fuel line to help avoid
vapor lock. Hot-weather grades of gasoline are blended
(1) Formation of Nucleus of Flame. As soon
from lower volatility fuels to lessen the tendency toward
as a spark jumps the gap of the spark plug electrode, a
vapor lock.
small ball of blue flame develops in the gap. This ball is
the first stage, or nucleus, of the flame. It enlarges with
d. Fuel Distribution.
When the fuel is not
relative slowness and,
distributed evenly to all cylinders, the engine will run
unevenly and power output will decrease. To ensure
good distribution, the fuel must be vaporized completely
and mixed with air in the manifold before entering the
combustion chamber.
must be removed during the refining process before
gasoline suitable for automotive use is produced. At one
time, considerable corrosion was caused by the sulfur
inherent in petroleum products, but modern refining
processes have made it almost negligible. Another
problem was the tendency for the hydrocarbons in the
gasoline to oxidize into a sticky gum when exposed to
air, which resulted in clogged carburetor passages, stuck
valves, and other operational difficulties. Chemicals that
control gumming are now added to gasoline. Dirt,
grease, water, and various chemicals also must be
removed to make gasoline an acceptable fuel.
Figure 4-76. Normal Combustion.
TA233436
4-39. Deicing Agents. Moisture in gasoline tends to
freeze in cold weather, causing clogged fuel lines and
carburetor idle ports. Deicing agents are added to
gasoline that mix with the moisture and act as an
antifreeze to prevent freezing.
4-40.
Antiknock Quality.
4-53
|
||
 |
||