
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 9-8000
Section II. COMPARISON OF ENGINE TYPES
2-11. Internal Combustion Engine Versus External
Combustion Engine.
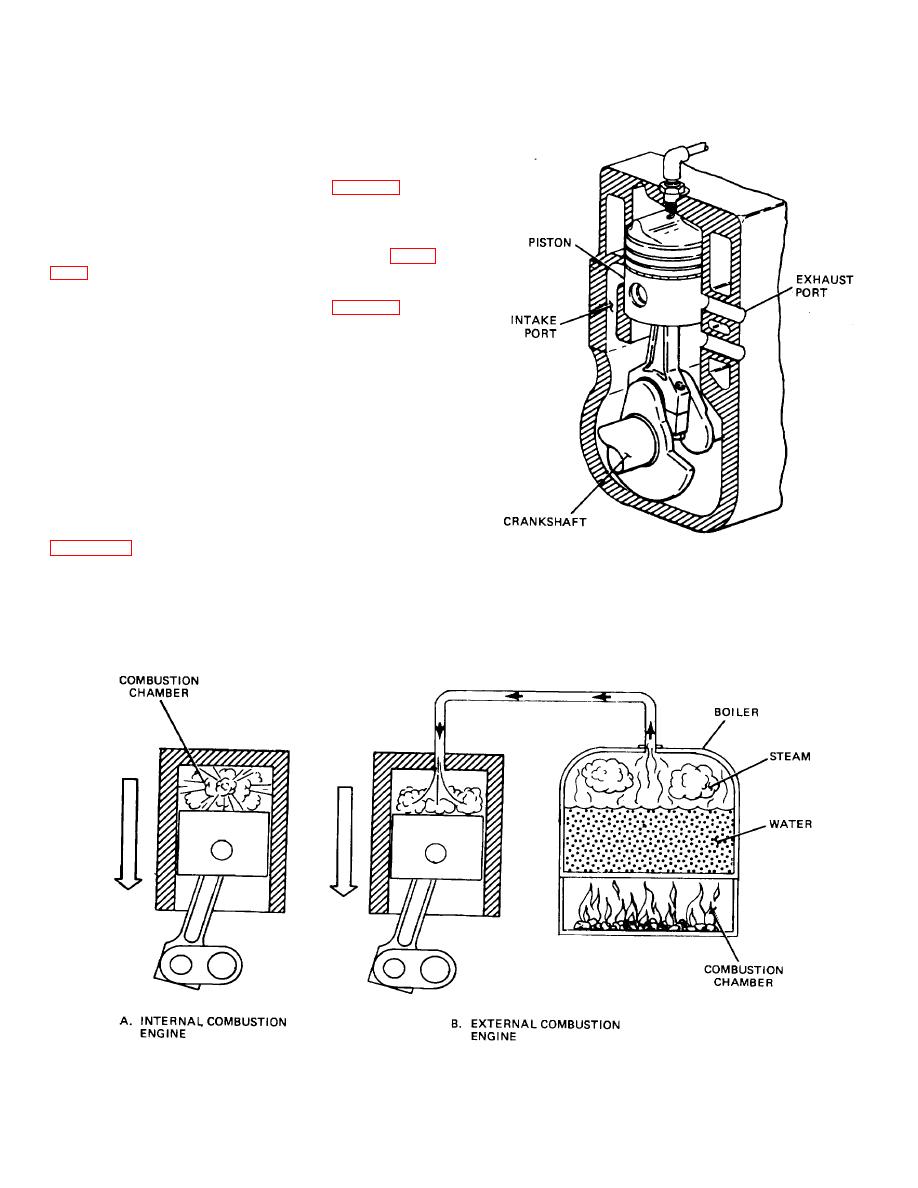
a. Internal Combustion Engine (A, Fig. 2-12). An
internal combustion engine is any engine in which the
fuel is burned within it. A four-stroke cycle engine is an
internal combustion engine because the combustion
chamber is located within the engine as shown in figure
b. External Combustion Engine (B, Fig. 2-12). An
external combustion engine is an engine in which the fuel
is burned outside of the engine. A steam engine is a
perfect example. The fuel is burned in an outside boiler,
where it makes steam. The steam is piped to the engine
to make it
run.
2-12. Four-Stroke Cycle Versus Two-Stroke Cycle.
The engine described in section I is a four-stroke cycle
engine. There is another form of gasoline piston engine
that has no valve mechanisms and completes one
operating cycle for every revolution of the crankshaft. It
is called a two-stroke cycle engine and is illustrated in
Figure 2-13. Two-Stroke Cycle Engine
In the combustion chamber, they are placed in the
cylinder wall. In this engine, the piston goes through a
power stroke every time it moves from top dead center to
bottom dead center. The
Figure 2-12. Internal Combustion Engine Versus External Combustion Engine
2-8
|
||
 |
||